This paper was written in 2019

Who are the intended audience for this paper?
Individuals who require ITIL framework basic knowledge and are in need to enhance IT service management in the Organization.
IT professionals (e.g. IT service manager, Directors, CIO’s, Business Manager, Support engineers and Business Process Owners) who want to adopt ITIL in order to make service improvement in the Organisation.
What is ITIL?
ITIL stands for Information Technology Infrastructure Library.
ITIL is commonly used for IT Service Management in the IT industry promoted by the service management industry experts.
The need for the ITIL was perceived by the end of the 1980s.
The British government had been facing problems in quality of IT service provided.
Hence it ordered the Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA) to come up with a framework for efficient use of IT resources within the British Government and the Private sector.
The CCTA started collecting and studying the best practices used across the industry for achieving better quality while reducing their costs to provision of IT Services.
What are the different versions of ITIL?
There are 4 versions of ITIL announced so far.
- ITIL v1 – The CCTA Developed ‘ITIL v1’ for Government IT operations in UK which was also called as “Government Infrastructure Management Method (GITMM)”. It included methods and best practices for Service Level Management strictly focused on client needs. It clearly defined the roles & responsibilities within the IT organizations and the IT processes. ITIL started with just 4 publications in v1. ITIL V1 consisted of a large number of separate books, each describing a particular process i.e. Service Level Management, Help Desk, Contingency Planning, Change Management.
During 2000 – 2001, the CCTA merged into the Office for Government Commerce (OGC). Microsoft used ITIL v1 as a basis to develop their proprietary Microsoft Operations Framework (MOF).
- ITIL v2 – This rapid growth of ITIL, lead to a new release of ‘ITIL v2’ in the year 2001. OGC ensured improvements to the original ITIL publication. The Service Support and Service Delivery books were redeveloped into more concise usable volumes. ITIL v2 was heavily process focused emphasizing what should be done to improve process.
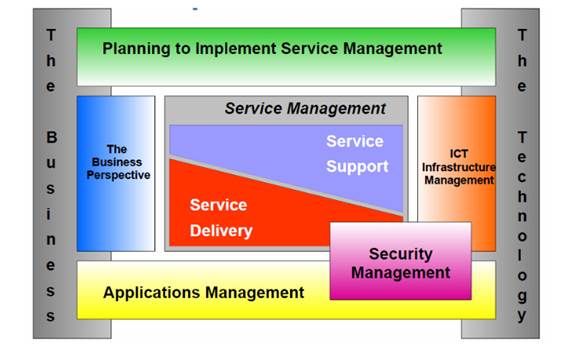
- ITIL v3 – In May 2007, OGC came up with the release of ‘ITIL v3’. During 2000 -20007 considerable changes were made in the IT Service Management. ITIL also evolved to meet the increasing complexities in the business environment. A lifecycle approach was invented to service management. It clearly explained how you should improve processes. It helped IT Departments focus on providing business value.
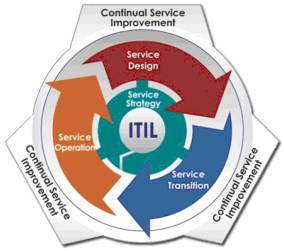
Difference between ITILv2 vs ITILv3
All the main processes as in ITIL v2 have been revised and enhanced in v3. with the addition of new Processes and Functions.
ITIL shifted from – “Modelling the organizations and their IT Service Management approach” to – “A Life Cycle approach to Service Management”.
- ITIL v4 – ITIL v4 released in February 2019 uses new techniques to bring IT to the next level of efficiency and effectiveness that aligns ITIL with other existing methods, including Agile, DevOps, and LeanIT. In version 4, the core elements of ITIL version 3 will remain essentially the same & inclusion additional best practices. ITIL v4 also further develops the concepts of value, service offerings, relationships, costs, risks, utility and warranty etc.
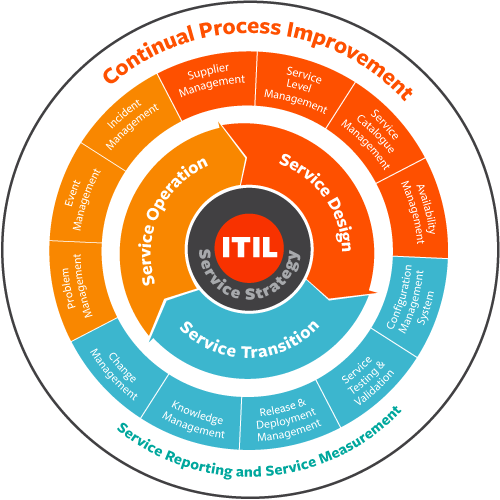
Key changes in ITIL v4
- The ITIL v3 processes are now referred as ITIL 4 practices.
- More emphasise on the “co-creation of value”
- The nine guiding principles of ITIL Practitioner are now seven
- Focus on value
- Start where you are
- Progress iteratively with feedback
- Collaborate and promote visibility
- Think and work holistically
- Keep it simple and practical
- Optimize and automate
The 4 Ps of service management are now referred as the 4 dimensions of service management
- Organizations and people
- Information and technology
- Partners and suppliers
- Value streams and processes

- The ITIL service lifecycle has been replaced with the ITIL service value system (SVS) and the service value chain within it.

- Automation process has been detailed in ITILv4.
What are the advantages of adopting ITILv4?
- ITIL v4 provides framework for ITSM.
- It provides strong alignment between IT and the business.
- Improves the productivity & Capability of IT staff by Implementing best practices to improve IT services, improve resources utilisation save costs.
- Improves the Customer satisfaction & delivery as well as relations between provider and consumer.
- Enables the business to keep pace with change and drive business change to its advantage.
Why should you implement ITIL in your business?
- Makes it easy to work with partners.
- It’ll make clear what your service desk can do, and can’t.
- Makes it easier to scale.
- Improves quality of service.
- Improved efficiencies on the floor.
References








